Hooks
object - Represent a set of functions (sync / async) to be called when form actions are processed. Object in resources object.
Example:
const resources = {
// ...
hooks: {
afterInit: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
beforeChangeValue: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterChangeValue: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterChangeData: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
}
};
Hooks usage
Access model object
Since the form model object is kept in the Form (class / ui library component), hooks can be used to gain access to the current model object in a specific lifecycle event.
Note: For
@jafar/react-form- hooks allow access to the form model object for non-child component, as supposed to child components that gain access using the form's context. The Form component can be located upper in the app's components tree to be supply access via context for more child components other than just the fields components. Locating the Form component in a higher location can have both advantage and disadvantage. The advantage is that it's data is available for more child component, and disadvantage is that each time the Form is updated and its state is updated - then all child components are re-rendered and that can hurt performance. This could be improved by using shouldComponentUpdate for child components (like we did with the Field component that only re-renders when the data that it needs was changed). Using hooks to gain access to the form model also has disadvantage that you might keep the data you need also in your app state and thats a duplication of data. So keep in mind that in order to gain access to the form model object sometimes the Form component can be higher and then use the form's context in the child component, and sometimes it can be lower and then use hooks.
Higher Form VS lower Form and using hooks
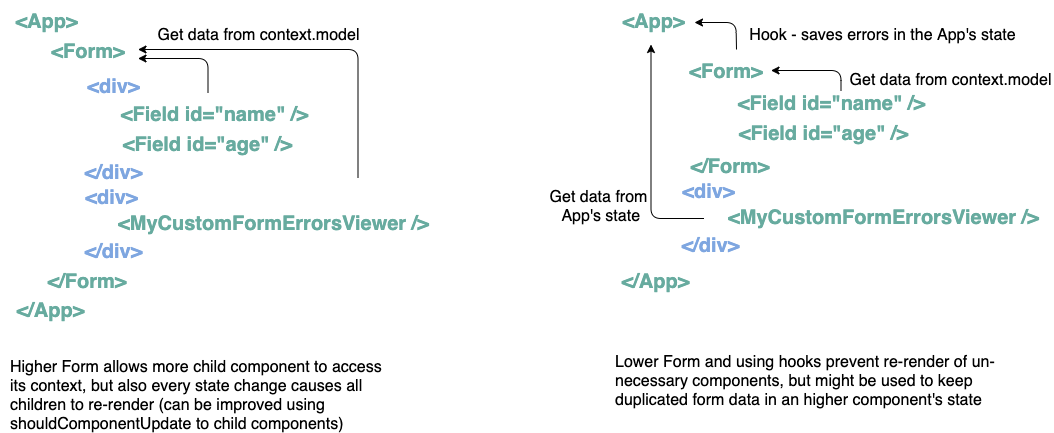
Tracking
Hooks can be used to track changes using the hooks arguments, for example when field value is changed - then the
formId, fieldId and value are available in the metadata argument of the before and after hooks.
During actions hooks
submit
Function (sync / async) is called during executing submit action, if the form is valid. Resolves to true on success.
submit: ({ data, context }) => {}
validate
Function (sync / async) is a form level validator which is called during execution of submit action (before calling submit hook - if no errors).
return undefined when form is valid or errors object ({ fieldId: [{ name, message }] }) when form is invalid.
validate: ({ data, context }) => {}
toDto
Function (sync / async) is called during executing init action and changeData action. Gets initial data (which originally defined in model.data - such as data object from the server) and should return new data object that the form will use and manipulate during its lifecycle.
toDto: ({ data }) => {} // return new form data
fromDto
Function (sync / async) is called during executing submit action. Gets form data (current model.data) and should return new data object (such as server structure data) that the form will pass to the submit hook.
fromDto: ({ data }) => {} // return new data to be passed to the submit hook
Note:
toDtoandfromDtoare not required definitions. You can also perform data conversions on the app level (before sending data to Jafar and after getting data from Jafar). Its just a convenient way to declare all form definitions in a single place.- You might be wondering about the different usage between
toDto & fromDtotoformatter & parser. Formatters and parsers only manipulate field value for the field's component, so only the component gets the formatted value (view value). But sometimes you might want to work on a more simple data structure during the form lifecycle (if the app data / server data was with complicated structure), such as in validators, excludeTerms, disableTerns and more form handlers. Fot that usertoDto & fromDto
isEmpty
Function (sync) determines if a field is considered empty. Its called during:
- Field validations - evaluates on
init,changeValue,changeDataactions. - Change value - during
changeValueaction, a value is unset from the form data object if its empty, otherwise sets to the data object. - empty term evaluation - evaluates on
init,changeValue,changeDataactions (only if defaultemptyterm was not overridden, and ifemptyterm was defined to one of the fields in either one of the terms such asexcludeTerm,disableTermandrequireTerms).
isEmpty: ({ id, value, dependencies: { id: { value } } }) => {}
By default - returns true for undefined, null, '', [] and {} values.
Note: Some system treat only
undefinedas an empty value. We strongly believe that any 'lake of data' should be considered empty and should be unset from the form's data object. Anyway this logic can be overridden.
emptyMessage
Function (sync) represent a required error message. Its called during field validation - evaluates on init, changeValue, changeData actions. If a field is empty and required, a required error (with message) is set to the field's errors, using this function's return value.
emptyMessage: ({ id, value, label, dependencies: { id: { value, label } } }) => {}
By default - returns Field invalid message.
Before / after actions hooks
beforeInit
Function (sync / async) is called before executing init action
beforeInit: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterInit
Function (sync / async) is called after executing init action
afterInit: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
beforeDestroy
Function (sync / async) is called before executing destroy action
beforeDestroy: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterDestroy
Function (sync / async) is called after executing destroy action
afterDestroy: ({ metadata, type }) => {}
beforeChangeData
Function (sync / async) is called before executing changeData action
beforeChangeData: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterChangeData
Function (sync / async) is called after executing changeData action
afterChangeData: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
beforeChangeValue
Function (sync / async) is called before executing changeValue action
beforeChangeValue: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterChangeValue
Function (sync / async) is called after executing changeValue action
afterChangeValue: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
beforeChangeState
Function (sync / async) is called before executing changeState action
beforeChangeState: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterChangeState
Function (sync / async) is called after executing changeState action
afterChangeState: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
beforeChangeUi
Function (sync / async) is called before executing changeUi action
beforeChangeUi: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterChangeUi
Function (sync / async) is called after executing changeUi action
afterChangeUi: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
beforeSubmit
Function (sync / async) is called before executing submit action
beforeSubmit: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterSubmit
Function (sync / async) is called after executing submit action
afterSubmit: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
Cross actions hooks
beforeAction
Function (sync / async) is called before executing any action
beforeAction: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterAction
Function (sync / async) is called after executing any action
afterAction: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
beforeDataChange
Function (sync / async) is called before executing any one of: init / changeValue / changeData / reset actions
beforeDataChange: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
afterDataChange
Function (sync / async) is called after executing any one of: init / changeValue / changeData / reset actions
afterDataChange: ({ model, resources metadata, type }) => {}
