Introduction
Managing complicated forms is a hard task for developers. Dealing with field validations, dependencies, disable or exclude fields in some conditions and more can make the code complicated, hard to maintain and hard to write to begin with.
Jafar let developers build forms easily by defining a readable and intuitive form definition (model json & resources json) that represent the entire form lifescycle - such as fields and their corresponding data path, initial data, validators, dto conversions and more. It's based on a pure javascript, ui free form class which handles the form's definition, lifecycle and data manipulations. With the basic form class, any ui library (such as react, angular and vue) can easily use it to expose Form and Field components.
Usage
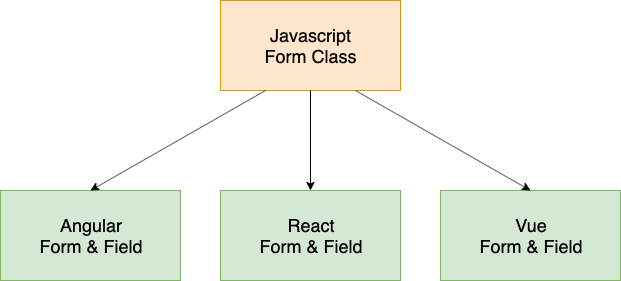
Supported Form Products
Form Class
Javascript Form class which manage fields and data manipulations. More info
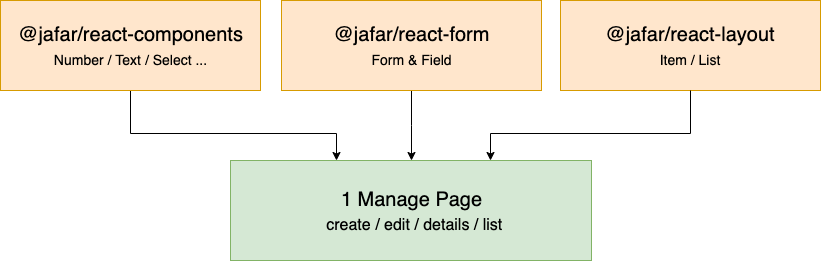
React
Supplies 3 products to manage forms in react applications. More info
- React Form & Field components based on Form class.
- Common components for usage such as Text, Number, Select and more, based on Material UI
- Layout components to build form pages / peaces with the same UI / UX experience such as Item component which contain header, sections, footer actions and menu actions.
Potentially a single page (edit / create / details / list) can be implemented using these 3 packages
Highlights
Manage Complicated Forms
Manage and maintain complicated form using a strait forward form definition (model & resources objects) which describes all the form settings and lifecycle such as:
- Validations
- Exclude term
- Disable term
- Dependencies
- UI settings
- Hooks
Framework Agnostic
Form Class - is a ui free javascript class that manages forms. Any UI library (such as React, Angular and Vue) can use it
as a base to create Form and Field components.
Our vision was to create a form definition model that will describe the entire form data and lifecycle in a simple persist json, so any developer that needs to maintain some forms will understand quickly what the form contains and doing only by a quick look on the json, without even getting into the code. This definition object will also help migrating an App UI library from React for example to some other UI library in no time since the form definition model object is the same for all UI libraries.
High Performance
- Jafar is based on a fast form javascript class.
- UI components such as react
Formcomponents updates its ui state for re-render only whenForm Classhad an UI related change. Fieldcomponent is updated only if relevant changes were made that affect it directly - i.e not all fields are re-rendered on each ui change.- Updating field value and state are protected with debouce, so the entire action lifecycle (such as changeValue) will not be triggered so many times. Having said that - the ui data do updates immediately without any debounce wait - to allow fast ui reaction to users.
- Actions such as changeValue and changeState that are done on the form wait in a queue to be processed to ensure data integrity - but the UI is updated immediately - to allow fast ui reaction to users.
Form Persistency
Define a form definition model object (json) as a first form state and pass it to the Form component.
It will be updated during the form's lifecycle. Get the updated form model after each action (using afterAction hook) and keep it in a local-storage. On page refresh - take the form model from
the local storage and pass it to the Form component in order to go back to the last state of the form - before the refresh.
Full Lifecycle Log
Form actions, such as changeValue is a set of multiple calculations. Each calculation result appears in a debug log
allowing the developer track each step of the form's actions. This level of transparency is very useful for debug and understand the underline
lifecycle of Jafar.
Track Actions
Jafar's Form hooks exposes afterAction hook among others. Use this hook that gets args such as action type and metadata - to track user actions on the form (such as change field value). For example use it to send to google analytics.
Replay Client Actions For Debug
Jafar's Form hooks exposes afterAction hook among others. Using this hook that gets args of the current form model and
action information - one can store the form's history of actions in order to log user actions. Later the actions history can be used to
automatically run the user's actions history in-order to track and debug reported bugs.
Form Snapshots and Undo Operations
Jafar's Form hooks exposes afterAction hook among others. Using this hook that gets args of the current form model (entire form snapshot) and action information - one can revert the form to its previous state by either one of the following options:
- Init Form again with previous form model
- Store the form actions and perform an opposite actions on demand. For example if previous field value was
aand now it changed tobusing the change value action - then it can be reverted by calling change value again with the previous valuea.
Server Side Validation
Any Node.js server can expose an endpoint that validates the same form definition that was already defined to the client pages, i.e - define the form validations only one time in one place (as suppose to cases where for example client validates the form using javascript and server validates the form using Java - different languages maintain, duplicate validations that might not be consists all the time).
Grid Usage
Use Jafar Form and Field components in each row of a grid - allowing each row to be both viewable and editable easily.
UI Components And Layout Supply
As suppose to other Form products - Jafar supplies entire management components for usage - in order to build manage pages quickly and with the same UI / UX experience.
React common components- such as Text, Number, Select and more.React layout components- such as Item (which can be used to build create / edit / details pages) and List (which can be used to build a list page)
Entity Templates
Create different form page templates using the same form definition - but using different sections definition for each view / template. For example - for 'Video' entity you can show different layouts / fields for different users depend on their role / permissions in the system. You can associate each template to a different user role / permissions.
Vast Documentation And Demos
Jafar is fully documented:
- All features and options
- Supported actions and their lifecycle logic that is implemented the same in the code
- Descriptive error for each invalid definition of form and lifecycle errors (such as defining circular field dependencies)
- Demo for each form scenario.
Low Dependencies Number
Form Class- that defined in@jafar/formis only usinglodashas a third-party dependency (it could have been implemented without any dependency but there is no need to reinvent the wheel).React Form Component- that defined in@jafar/react-formis only using@jafar/formas a dependency.React Components and Layout- using React Material UI as underline components.
Small Package Size
Jafar's packages don't not contain a lot of code, therefor are light and don't affect much the app's bundle size.
High Test Coverage
High unit tests coverage and cover each form demo with an e2e test.
