Formatter & Parser
Define formatter and parser to a field component definition when the field's value structure is different then the structure that the component can handle.
For example - if a field 'birthDate' value is a string and its component of 'DatePicker' can only accept Date() objects.
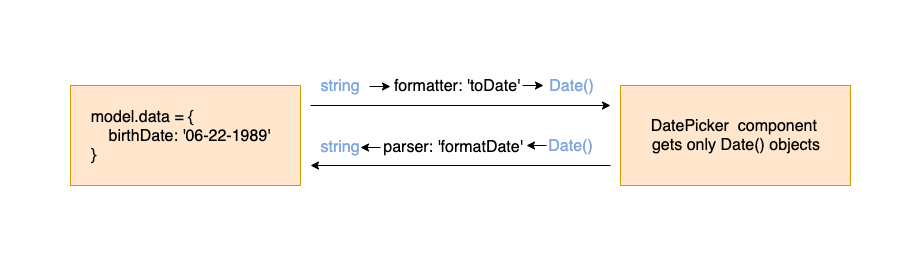
Field Formatter Parser
To define field component formatter and parser - a definition is required in model.fields.someField.component object, and implementation is required in resources.conversions object.
Note: Define both formatter and parser if the field uses editable component (i.e component calls change value), and only formatter if the field uses readonly component (i.e component doesn't call change value).
Model
model.fields.someField.formatter and model.fields.someField.parser- object. Contains:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | required string | Represents the key in resources.conversions object |
| args | object | Custom data to pass to the conversion function |
Resources
resources.conversions - object. Required only if formatter or parser defined in at least one of the fields.
Key is the conversion name, and value is an object that contains:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| func | required function | Gets a value and return new value. Function can be sync or async function (that resolves to a new value). More info |
| defaultArgs | object | Default args for all fields. This will be shallow merged with field level conversion args before passed to the func |
func
function ({
id,
value,
state,
dependencies { id: { value } },
args,
context,
})
return value -
- When used by
formatter- value is thedata value(from model.data) and return value is the formatted value (view value for component). - When used by
parser- value is theview value(from component) and return value is the parsed value (data value).
Example
consider birthDate field which uses DatePicker component, which accepts only Date() objects, but your model.data.birthDate is a string value that represent a date in the server. So, field birthDate should define:
- A formatter function that gets the data value (string date) and return it as Date() object (then
DatePickercomponent can accept it). - A parser function that gets the view value (date object from the component) and return it as string (then it will be set back in the model.data).
import DatePicker from '../myComponents/DatePicker';
import dateformat from 'dateformat';
const model = {
fields: {
birthDate: {
// ...
component: {
name: 'DatePicker',
},
formatter: { name: 'toDate' },
parser: { name: 'formatDate', args: { format: 'mm/dd/yyyy' } },
}
},
data: {
birthDate: '06/22/1989',
}
};
// Note: both 'toDate' and 'formatDate' are built-in conversions and are not required here.
// We added them just for the example.
const resources = {
components: {
DatePicker: {
renderer: DatePicker
},
},
conversions: {
toDate: {
func: (props) => { // return Date()
return new Date(props.value); // here 'props.value' is the data value (string) taken from model.data
}
},
formatDate: {
defaultArgs: { format: 'mm-dd-yyyy' }, // can be overridden by field level args
func: (props) => { // return string
return dateformat(props.value, props.args.format); // here 'props.value' is the view value (Date object) from the component
}
}
}
};
Shorthand
Definition shorthand for formatters / parsers can be found in definition shorthand documentation.
Built-in Conversions
Jafar also defines built-in conversions: 'toString', 'toNumber' and so on.
Built-in conversions work out of the box, there's no need to define them in resources.conversions.
Jafar extends custom resources.conversions object with the built-in conversions object.
Examples:
- Define
formatter/parserconversion that is not part of the built-in conversions. In this case - conversions functions should be supplied inresources.conversionsobject:
const model = {
// ...
fields: {
// ...
birthDate: {
// ...
component :{
// ...
},
formatter: { name: 'myFormatter' },
parser: { name: 'myParser' },
}
},
};
const resources = {
conversions = {
myFormatter: {
func: (props) => {
// ...
},
},
myParser: {
defaultArgs: { // defaultArgs are not required
// ...
}
func: (props) => {
// ...
},
}
}
}
- Define
formatter/parserconversion that is part of the built-in conversion. In this case there is not need to supply conversion inresources.conversionsobject:
const model = {
// ...
fields: {
// ...
age: {
// ...
component :{
// ...
},
formatter: { name: 'toNumber' },
parser: { name: 'toString' },
}
},
data: {
age: '18', // as is string in the database
}
};
// no need to define resources.conversions
- Define
formatter/parserconversion that is part of the built-in conversion and also define it inresources.conversionsobject in order to override the built-in function behavior (can overridefunc/args/both):
const model = {
// ...
fields: {
// ...
age: {
// ...
component :{
// ...
},
formatter: { name: 'toNumber' },
parser: { name: 'toString' },
},
},
data: {
age: '18', // as is string in the database
}
};
const resources = {
conversions: {
toString: { // override the default build in conversion 'toString'. You can also supply defaultArgs or only supply defaultArgs
func: props => {
// return ...
}
}
}
};
The following are Jafar's built-in conversions and their usage:
toString
Convert value to string representation.
Expected value:
string / number / boolean / Date() / null / undefined
Returns:
string- if value isstring/number/boolean/Date()undefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Example:
Age field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets number values
// model.fields.age
formatter: { name: 'toNumber' }
parser: { name: 'toString' }
// model.data
data: { age: '18' }
toNumber
Convert value to number representation.
Expected value:
string / number / boolean / Date() / null / undefined
Returns:
number- if value isstring/number/boolean/Date()undefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Example:
Age field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets number values
// model.fields.age
formatter: { name: 'toNumber' }
parser: { name: 'toString' }
// model.data
data: { age: '18' }
toDate
Convert value to Date() representation.
Expected value:
string / number / Date() / null / undefined
Returns:
Date()- if value isstring/number/Date()undefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Example:
Birthdate field has a number representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets date values
// model.fields.birthDate
formatter: { name: 'toDate' }
parser: { name: 'toNumber' }
// model.data
data: { birthDate: 1575715837659 }
toBoolean
Convert value to boolean representation.
Expected value:
string / number / boolean / null / undefined
Returns:
boolean- if value isstring/number/boolean/null/undefined
Example:
CanViewVideo field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets boolean values
// model.fields.canViewVideo
formatter: { name: 'toBoolean' }
parser: { name: 'toString' }
// model.data
data: { canViewVideo: 'true' }
formatDate
Convert value to formatted date string.
Expected value:
Date() / null / undefined
Returns:
string- if value is Date()objectundefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| format | string | 'mm-dd-yyyy' | Format of a date in a string representation |
Example:
Birthdate field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets Date() values
// model.fields.birthDate
formatter: { name: 'toDate' }
parser: { name: 'formatDate', args: { format: 'mm/dd/yyyy' } }
// model.data
data: { birthDate: '06/22/1989' }
split
Convert value to array representation containing split parts of value.
Expected value:
string / null / undefined
Returns:
string array- if value isstringundefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| separator | string | ',' | Separates value using this |
Example:
Friends field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets array values
// model.fields.friends
formatter: { name: 'split', args: { separator: ';' } } // default separator is ','
parser: { name: 'join', args: { separator: ';' } }
// model.data
data: { friends: 'Rachel;Ross;Monica' }
// split will return ['Rachel', 'Ross', 'Monica']
join
Convert value to string representation containing joined parts of value.
Expected value:
array / null / undefined
Returns:
string- if value isarrayundefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| separator | string | ',' | Join value using this |
| path | string | undefined | If array is array of objects - define a path to the sub data to join for each object in the array |
Example:
- Friends field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets array values
// model.fields.friends
formatter: { name: 'split', args: { separator: ';' } } // default separator is ','
parser: { name: 'join', args: { separator: ';' } }
// model.data
data: { friends: 'Rachel;Ross;Monica' }
// split will return ['Rachel', 'Ross', 'Monica']
- Friends field has an objects array representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets string value
// model.fields.friends
formatter: { name: 'join', args: { path: 'name', separator: ', ' } }
// model.data
data: {
friends: [
{ name: 'Rachel'},
{ name: 'Monica' },
{ name: 'Ross' }
];
}
// join will return 'Rachel, Monica, Ross'
joinKeys
Convert keys of value to string representation containing joined parts of value's keys.
Expected value:
object / null / undefined
Returns:
string- if value isobjectundefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| separator | string | ',' | Join value using this |
Example:
Colors field has an object representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets string
// model.fields.colors
formatter: { name: 'joinKeys', args: { separator: ', ' } } // default separator is ','
// model.data
data: {
colors: {
RED: 'Red',
BLUE: 'Blue',
GREEN: 'Green'
}
}
// joinKeys will return 'RED, BLUE, GREEN'
joinValues
Convert values of value to string representation containing joined parts of value's values.
Expected value:
object / null / undefined
Returns:
string- if value isobjectundefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| separator | string | ',' | Join value using this |
| path | string | undefined | Define a path to the sub data to join each object in the object values |
Example:
- Colors field has an object representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets string
// model.fields.colors
formatter: { name: 'joinValues', args: { separator: ', ' } } // default separator is ','
// model.data
data: {
colors: {
RED: 'Red',
BLUE: 'Blue',
GREEN: 'Green'
}
}
// joinValues will return 'Red, Blue, Green'
- Colors field has an object representation in the model.data, but uses a component that only gets string
// model.fields.colors
formatter: { name: 'joinValues', args: { separator: ', ', path: 'label' } } // default separator is ','
// model.data
data: {
colors: {
RED: { label: 'Red' },
BLUE: { label: 'Blue' },
GREEN: { label: 'Green' }
}
}
// joinValues will return 'Red, Blue, Green'
jsonStringify
Convert value to json string representation.
Expected value:
any / undefined
Returns:
undefined- if value isundefinedstring- if value isany
Example:
CustomDate field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a json editor component that only gets object values
// model.fields.customDate
formatter: { name: 'jsonParse' }
parser: { name: 'jsonStringify' }
// model.data
data: {
customData: '{"name":"Rachel","age":25}'
}
// jsonParse will return {
// name: "Rachel",
// age: 25,
// }
jsonParse
Convert value to object.
Expected value:
string / null / undefined
Returns:
object- if value is stringifiedstringundefined- if value isundefinednull- if value isnull
Example:
CustomDate field has a string representation in the model.data, but uses a json editor component that only gets object values
// model.fields.customDate
formatter: { name: 'jsonParse' }
parser: { name: 'jsonStringify' }
// model.data
data: {
customData: '{"name":"Rachel","age":25}'
}
// jsonParse will return {
// name: "Rachel",
// age: 25,
// }
