Validators
Define validtors in a form in order to protect and verify form / field validity. Jafar evaluates validators during its lifecycle, and sets invalid result flag to a field / form.
Field Level Validators
Field level validators are evaluated on init and on field value change (only changed fields and their dependencies are evaluated on a change).
To define field level validators - a definition is required in the model.fields.someField object, and implementation is
required in the resources.validators object.
Validators are evaluated only if the field is not empty.
Note: required is a special validation which is defined directly under
field.required = true, and not in the validators array.
Note: Field level validators can be either
syncorasyncfunctions. Those validators are being evaluated each time a field (or fields that is depend on) is changed. For eachasyncvalidator think carefully whether it should be in a field level, or should be called only one time during submit action (by verifying it in form level validation) - to avoid massive calls to the server.
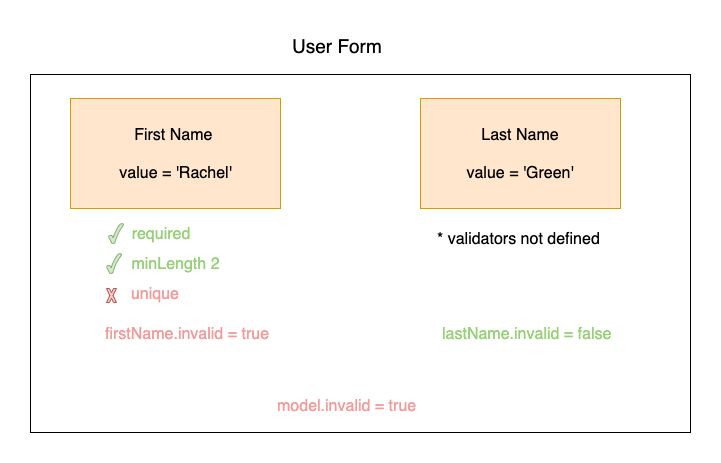
Validation Logic
Validations logic during a field evaluation can be found in validation logic.
Model
model.fields.someField.validators - object array. Set of objects which describe validators that evaluate on each field value (or one of its dependencies) change.
A field is valid when all of the validator functions return true (or has no validators at all).
The order of validators corresponds to the order that field.errors appear.
Each validator object contains:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | required string | Represent the key in resources.validators object |
| args | object | Custom data to pass to the validator and message functions |
Resources
resources.validators - object. Required only if model.fields.someField.validators is defined.
Key is the validator name, and value is an object that contains:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| func | required function | Returns if validation is valid. Function can be sync or async function (that resolves to the result). More info |
| message | required function | Returns a string error message in case the validation function returns invalid. Function can be sync or async function (that resolves to a result value). More info |
| defaultArgs | object | Default args for all fields. This will be shallow merged with field level conversion args before passed to the func / message |
func
function ({
id,
value,
dependencies { id: { value } },
args,
context,
})
return value options:
- boolean: return
truefor valid, otherwisefalse. - object: return structure like
{ valid: false, args: { invalidSites: ['bla', 'blu'] } }. Args are dynamic args which is passed to the message function (assigned to the message args object).
message
function ({
id,
value,
label
dependencies { id: { value, label } },
args, // result of defaultArgs, field level args, and dynamic args (from the func)
context,
})
return value - string error message.
Example
Name field is required, requires a value with minimum length of 2 chars, and unique in the database:
import MyService from './MyService';
const model = {
// ...
fields: {
// ...
name: {
// ...
required: true,
validators: [{
name: 'minLength' // a key in resources.validators object
args: {
value: 2
}
}, {
name: 'uniqueField', // a key in resources.validators object
args: {
serverField: 'userName',
},
}]
}
},
};
// note - 'minLength' is a built-in validator - therefor not needed here
const resources = {
// ...
validators: {
uniqueField: {
func: async (props) => { // props = { id, value, dependencies { id: value }, args, context }
return await MyService.isFieldUnique(props.args.serverField, props.value); // async call, resolves to true / false
},
message: (props) => {
return `${props.label} should be unique`;
}
}
},
};
Shorthand
Definition shorthand for validators can be found in definition shorthand documentation.
Built-in validators
Jafar offers built-in validators, like 'minLength', 'maxLength' and etc.
There is no need to define them in your resources.validators object.
The custom validators object (resources.validators) extends Jafar's built-in validators.
There are several ways to extend the built-in validators:
- Define in
model.fields.someField.validatorsarray some built-in validators.
Example
const model = {
// ...
fields: {
// ...
name: {
// ...
validators: [ {
name: 'minLength',
args: {
value: 2
},
}]
}
},
}
// no need for resources.validators object
- Define in
resources.validatorsobject some custom validators that are not part of the built-in validators:
Example
import services from './services';
const model = {
// ...
fields: {
// ...
name: {
// ...
validators: [{
name: 'uniqueName'
}]
}
},
};
const resources = {
validators: {
uniqueName: {
defaultArgs: {
entityType: 'EMPLOYEE',
}
func: async (props) => {
const items = await services[props.args.entityType].search({ name: props.value || '' });
return items.length === 0;
},
message: (props) => {
return `${props.label} should be unique`;
}
}
}
};
- Override in
resources.validatorsobject a built-in validator with custom functions and messages:
resources.validators = {
minLength: {
defaultArgs: {
myMinimum: '1',
}
func: (props) => {
return props.value.length < props.args.myMinimum;
},
message: (props) => {
return `Yo! Field '${props.label}' should have minimum length of ${props.args.myMinimum} dude!`;
}
}
}
}
- If
resources.validatorsobject defines a built-in validator, you can also define a custom override for only some of message / func / defaultArgs:
resources.validators = {
minLength: {
message: (props) => {
return `Yo! Field '${props.label}' should have minimum length of ${props.args.value} dude!`;
}
}
}
}
The following are Jafar's built-in validators and their usage:
minLength
Verify that field's value.length is greater or equals to args.value
Expected value:
array / string
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | number | 0 | Field's value.length should be greater or equals to this |
Example:
Verify value of name field contains value of minimum length of 2 (for values that have "length" property)
// model.fields.name.validators
validators: [{
name: 'minLength',
args: {
value: 2,
}
}]
// error: 'Minimum length is 2'
maxLength
Verify that field's value.length is lower or equals to args.value
Expected value:
array / string
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | number | 0 | Field's value.length should be lower or equals to this |
Example:
Verify value of name field contains value of maximum length of 10 (for values that have "length" property)
// model.fields.name.validators
validators: [{
name: 'maxLength',
args: {
value: 10,
}
}]
// error: 'Maximum length is 10'
min
Verify that field's value is greater or equals to args.value
Expected value:
number
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | number | 0 | Field's value should be greater or equals to this |
Example:
Verify age field value is at least 18.
// model.fields.age.validators
validators: [{
name: 'min',
args: {
value: 18,
}
}]
// error: 'Minimum value is 18'
max
Verify that field's value is lower or equals to args.value
Expected value:
number
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | number | 0 | Field's value should be lower or equals to this |
Example:
Verify age field is 30 at most.
// model.fields.age.validators
validators: [{
name: 'max',
args: {
value: 30,
}
}]
// error: 'Maximum value is 30'
between
Verify that field's value is greater or equals to args.min and lower or equals to args.max
Expected value:
number
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| min | number | 0 | Field's value should be greater or equals to this |
| max | number | 0 | Field's value should be lower or equals to this |
Example:
Verify age is between 18 and 30.
// model.fields.age.validators
validators: [{
name: 'between',
args: {
min: 18,
max: 30,
}
}]
// error: 'Value should be between 18 - 30'
url
Verify that field's value is a valid url.
Expected value:
string
Example:
Verify facebookUrl is a valid url.
// model.fields.facebookUrl.validators
validators: [{
name: 'url',
}]
// error: 'Invalid url'
Verify that field's value is a valid email.
Expected value:
string
Example:
Verify userEmail is a valid email.
// model.fields.userEmail.validators
validators: [{
name: 'email',
}]
// error: 'Invalid email'
match
Verify that field's value matches args.value (which is regular expression).
Expected value:
string
Default args:
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | regex | /^(.*)$/ | Field's value should match to this |
Example:
Verify greeting matches /^Hello (.*)$/ (string with prefix of Hello).
// model.fields.greeting.validators
validators: [{
name: 'match',
args: {
value: /^Hello (.*)$/,
}
}]
// error: 'Invalid match to: /^Hello (.*)$/'
Form Level Validator
Define validate hook in order to have a form level validator. Function (sync / async) is called during execution of submit action (before calling submit hook - if no errors).
Form level validator function gets as arg the entire form data object.
Return undefined when form is valid or errors object ({ fieldId: [{ name, message }] }) when form is invalid.
Example
import Form from '@jafar/form';
const model = {
// ...
fields: {
// ...
email: {
// ...
path: 'email',
},
},
};
const resources = {
hooks: {
validate: async ({ data }) => {
// do some sync / async validations...
const isUnique = await UserService.isEmailUnique(data.email);
// and return errors (or undefined if form is valid)
return isUnique ? undefined : {
email: [{
name: 'uniqueField',
message: 'Email already exists',
}];
},
},
submit: ({ data }) => {
UserService.sava(data);
},
},
},
const form = new Form();
await form.init(model, resources);
// change email to value that is not unique
form.changeValue('email', 'something@notunique.com');
// call submit (during submit action the validate hook is called ->
// and then if no errors the submit hook is called)
const success = await form.submit();
// verify submit failed
expect(success).toBeFalsy();
// verify field errors and invalid
expect(form.fields.email.invalid).toBeTruthy();
expect(form.fields.email.errors).toEqual([{
name: 'uniqueField',
message: 'Email already exists',
}]);
// verify form errors and invalid
expect(form.invalid).toBeTruthy();
expect(form.errors).toEqual({
email:[{
name: 'uniqueField',
message: 'Email already exists',
}],
});
// change email to value that is not unique
form.changeValue('email', 'something@unique.com');
// call submit
const success = await form.submit();
// verify submit success
expect(success).toEqual(true);
